Understanding the buyer journey is essential for any business aiming to improve its marketing and sales strategies. This journey outlines the process customers go through before making a purchase. It starts when they first identify a need and ends when they make a purchase decision.
Each stage of the buyer’s journey stages requires specific strategies to effectively guide potential customers towards making a purchase.
For businesses, especially in B2B markets, grasping the b2b buyer journey is crucial. The complexities of b2b sales journey often involve multiple decision-makers and a longer decision-making process.
Similarly, understanding the customer buyer journey helps in tailoring interactions that resonate on a personal level, influencing buying decisions positively.
Furthermore, the knowledge gained from this journey aids businesses in creating a customer persona and journey development. By mapping out buyer stages and marketing journey stages, companies can craft more targeted, effective marketing messages.
This strategic approach not only improves the alignment of marketing efforts but also enhances the overall efficiency of the sales process.
In summary, whether you’re refining your sales journey or looking to develop deeper customer insights, understanding the buyer’s journey provides a foundation for creating stronger, more effective customer relationships.
The Stages of the Buyer’s Journey
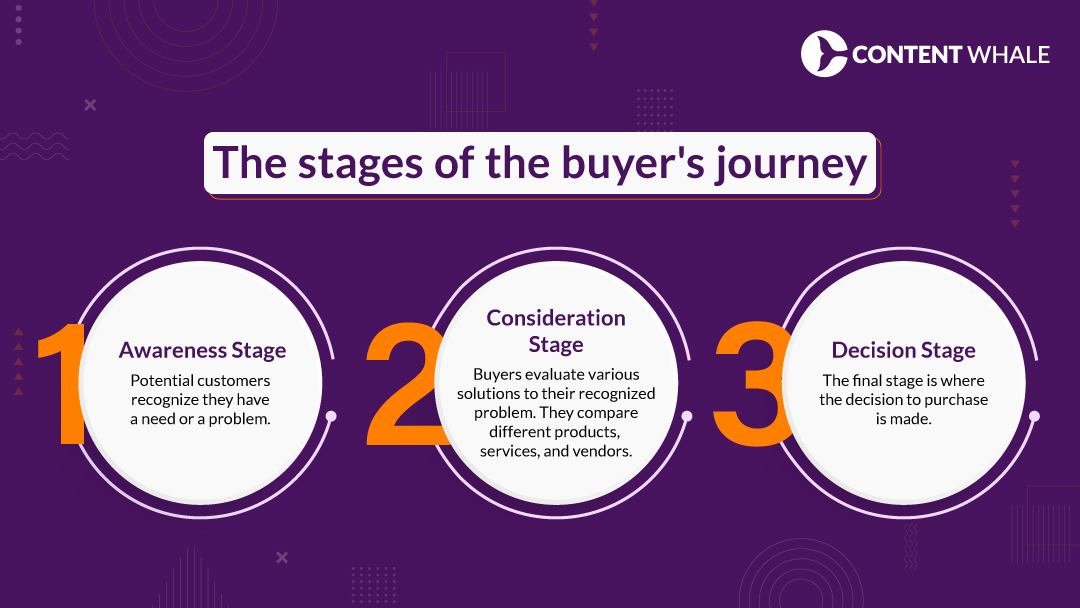
The buyer journey involves several critical stages. Each stage represents a different part of the customer’s purchasing process. By understanding these stages, companies can create more effective marketing and sales strategies.
1. Awareness Stage
This is the beginning of the buyer’s journey stages. Potential customers recognize they have a need or a problem.
At this stage, it’s vital for businesses to provide informative content that helps prospects identify their issues. This content sets the stage for deeper engagement.
2. Consideration Stage
Here, buyers evaluate various solutions to their recognized problem. They compare different products, services, and vendors.
Businesses should focus on content that highlights the advantages and unique features of their solutions. This is a key moment to differentiate from competitors.
3. Decision Stage
The final stage is where the decision to purchase is made. Effective strategies at this point address potential concerns and clearly demonstrate the value of the chosen solution.
Companies need to ensure that all information necessary to facilitate a purchase decision is readily available.
Throughout the b2b buyer journey and customer buyer journey, each interaction is an opportunity to influence the decision-making process.
By mapping these buyer stages accurately and tailoring content accordingly, businesses can significantly improve their sales journey and marketing journey stages.
For companies looking to create a customer persona and journey development, understanding these stages helps tailor marketing efforts to meet the specific needs of different customer segments.
This approach ensures that marketing resources are used more efficiently, leading to better conversion rates and higher customer satisfaction.
B2B Buyer Journey

The B2B buyer journey is distinctively intricate compared to B2C models. It requires an understanding of complex buying dynamics and longer decision-making processes.
1. Distinct Characteristics
The b2b buyer journey often involves multiple stakeholders. Each has specific roles and influences at various buyer’s journey stages. The decision-making process is thus extended, as consensus is required from various departments.
2. Role of Content and Communication
Effective communication is key across all buyer stages. Businesses need to provide detailed, industry-specific content that addresses the unique concerns of each stakeholder. This includes technical data, case studies, and ROI analyses.
3. Relationship Management
Building and maintaining strong relationships is crucial throughout the b2b sales journey. Trust and reliability are more significant in B2B environments, where purchases often have higher stakes.
4. Impact of Multiple Decision-Makers
The involvement of multiple decision-makers introduces complexity but also presents an opportunity. Businesses can tailor their marketing to address the diverse needs and concerns of each decision-maker.
5. Longer Sales Cycles
The sales journey in a B2B context is usually longer. Companies must nurture leads over time, often requiring several interactions before a purchase decision is made. Patience and persistence in follow-ups are vital.
By focusing on these elements, businesses can effectively navigate the B2B buyer journey. This careful attention to detail ensures that the strategies align with the complex dynamics of B2B purchasing, enhancing the chances of successful transactions.
B2C Buyer Journey

The B2C buyer journey tends to be more straightforward and faster than the B2B buyer journey. Emotional triggers and quick decision-making are central features of this journey.
1. Overview of B2C Operations
The customer buyer journey in B2C markets typically involves fewer steps before purchase. Consumers often make decisions quickly, influenced by effective branding and marketing.
- Key Differences in Decision-Making: Unlike B2B, B2C buyers usually decide independently or with minimal consultation. This makes the emotional appeal and immediate benefits crucial in marketing efforts.
- Strategies for Quick Conversions: Marketers should leverage strong, emotional content that connects quickly with the consumer. Offers, discounts, and strong call-to-actions are effective in driving rapid decisions.
Understanding these key components allows businesses to tailor their strategies effectively throughout the sales journey. This ensures that marketing efforts meet the unique needs of B2C consumers, leading to higher conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
2. Creating Effective Customer Personas
Creating a customer persona and journey development is crucial for targeting marketing efforts accurately. This process involves gathering and analyzing data to understand diverse customer needs and behaviors.
- Developing Detailed Personas: Start by collecting data through surveys, interviews, and digital analytics. Use this information to create personas that represent typical buyers in both B2B and B2C settings.
- Utilizing Data and Feedback: Regularly update personas with new data and customer feedback. This helps ensure that marketing strategies remain aligned with changing customer preferences and behaviors across different buyer stages.
3. Example Personas for B2B and B2C Buyer Journeys
Creating detailed personas is a strategic approach that helps businesses better understand their customers. Here are examples for both B2B and B2C contexts:
a) B2B Persona: IT Manager Mark
- Demographics: Age 42, male, married, lives in a suburban area.
- Professional Role: IT Manager at a mid-sized enterprise.
- Goals: Seeks to streamline IT operations, enhance system security, and reduce overhead costs.
- Challenges: Faces budget constraints, pressure to adopt new technologies, and the need to manage a diverse team.
- Decision-making style: Prefers detailed, technical content and case studies. Values vendor reputation and post-sales support.
- Preferred Content: Whitepapers, tech blogs, product comparison guides.
b) B2C Persona: College Student Emily
- Demographics: Age 20, female, single, urban dweller, college sophomore.
- Interests: Enjoys fashion, technology, and social media.
- Goals: Looks for trendy, affordable fashion and gadgets. Wants quick, easy shopping experiences.
- Challenges: Limited budget, needs products that offer good value for money.
- Buying Behavior: Influenced by peer recommendations and social media ads.
- Preferred Content: Short promotional videos, influencer collaborations, and flash sale notifications.
These personas help tailor the buyer journey by highlighting specific needs, preferences, and typical behaviors that guide marketing strategies. For the B2B buyer journey, understanding a persona like IT Manager Mark helps in creating content that addresses technical needs and offers long-term solutions.
For the customer buyer journey in B2C, knowing what drives a college student like Emily aids in designing campaigns that are visually appealing and highlight immediate benefits. This level of detail in persona development ensures that marketing efforts across buyer stages and marketing journey stages are more effective and closely aligned with the customer’s expectations and needs.
This methodical approach to persona development enhances the effectiveness of the buyer journey by ensuring that all marketing activities are specifically tailored to meet the identified needs of different customer segments.
Mapping and Optimizing the Buyer’s Journey

Mapping the buyer journey involves visualizing the path potential customers take from awareness to purchase. Effective mapping enhances marketing and sales strategies, significantly impacting customer engagement and conversion rates.
1. Techniques to Map the Journey
- Identify Key Stages: Clearly define the stages of the buyer’s journey stages, such as awareness, consideration, and decision. For each stage, identify the customer’s goals, questions, and potential barriers.
- Gather Data: Use tools like Google Analytics, customer surveys, and CRM data to understand how customers move through your sales funnel. Look for common patterns or drop-off points that need attention.
- Visualize the Journey: Create visual representations of the journey using flowcharts or journey maps. This should include all touchpoints where customers interact with your brand, such as social media, email, or customer service calls.
2. Content and Strategies for Each Stage
- Awareness Stage: Focus on educational content that helps potential customers recognize their needs. Use blog posts, infographics, and videos to raise awareness about their problems and your solutions.
- Consideration Stage: Provide comparative analyses, expert guides, and product demos to help customers evaluate your offerings against their needs. For B2B contexts, detailed case studies and technical webinars work well to demonstrate the value and functionality of your solutions.
- Decision Stage: Offer testimonials, reviews, and strong call-to-action (CTA) elements that encourage a purchase decision. Ensure that your sales team is equipped to handle objections and provide personalized follow-ups.
3. Examples of Successful Mapping
a) Rewind – B2B SaaS Customer Journey Map
Rewind, a company that makes backup and restoration software for SaaS platforms, mapped out their B2B SaaS customer journey to address shortcomings in attracting the ideal customer. They started by defining their ideal customer profile and conducting in-depth customer interviews to understand buyer motivations and decision-making processes.
By integrating tools like Google Analytics and HubSpot, they gained insights into how users interacted with their marketing materials online, especially focusing on the high-intent, back-and-forth journey that occurs mostly online. This thorough mapping helped Rewind discover new buyer motivations, leading to a revised go-to-market strategy, improved product positioning, and ultimately a two-fold increase in product installations.
b) Spotify – B2C Digital Customer Journey Map
Spotify conducted an extensive mapping of their customer journey focusing on one specific feature: sharing playlists via third-party apps. The journey mapping research highlighted a significant customer pain point—the fear of being judged for their music taste—and identified an awareness gap among users about the feature.
By refining their in-app user interfaces and streamlining the customer experience for playlist sharing, Spotify not only enhanced usability but also bolstered customer engagement and loyalty.
c) Amazon – E-commerce Customer Journey Map
Amazon’s approach to customer journey mapping involves monitoring detailed success metrics at each stage of the customer journey. Metrics like impressions, click-through rates, add-to-cart rates, and repeat purchase rates help Amazon gain a deep understanding of customer interactions and behaviors throughout their shopping experience.
This methodical tracking allows Amazon to optimize each step of the journey, ensuring a seamless shopping experience that drives conversions and customer retention.
| Company | Industry | Focus of Mapping | Key Actions | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rewind | B2B SaaS | Entire B2B purchase process | Defined ideal customer profile, conducted customer interviews, used analytics for insights | Improved go-to-market strategy, doubled product installations |
| Spotify | B2C Digital | Playlist sharing via apps | Identified customer pain points and awareness gaps, refined in-app UI | Enhanced usability and customer engagement |
| Amazon | E-commerce | Overall shopping experience | Monitored detailed success metrics at each journey stage | Optimized shopping experience, improved conversion and retention rates |
These examples illustrate the effectiveness of detailed customer journey mapping in both B2B and B2C contexts. By understanding and addressing specific customer behaviors, needs, and pain points at each stage of the journey, companies like Rewind, Spotify, and Amazon have successfully enhanced their marketing strategies and improved overall business performance.
Optimizing the buyer journey ensures that potential customers receive the right message at the right time, making the path to purchase as smooth and efficient as possible. This strategic approach not only improves the customer experience but also increases the effectiveness of marketing budgets by focusing efforts where they are most likely to yield results.
How to Enhance the Buyer’s Journey: Tools and Techniques

1. CRM Systems
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are essential for tracking interactions with potential and existing customers. They help businesses understand customer behaviors and preferences throughout the b2b buyer journey and customer buyer journey.
- Salesforce: Offers comprehensive features for customer management, sales tracking, and marketing automation.
- HubSpot CRM: Known for its user-friendly interface and deep integration capabilities with marketing, sales, and service hubs.
- Zoho CRM: Provides a wide range of features including sales automation, performance analytics, and multichannel communication.
2. Marketing Automation
Automation tools can deliver targeted messages at optimal times. They are vital for nurturing leads through the sales journey, especially in complex b2b sales journey scenarios where multiple touchpoints are involved.
- Marketo: Well-regarded for its lead management, email marketing, and revenue attribution features, making it ideal for b2b sales journeys.
- Mailchimp: Offers strong email marketing tools and automation features that are easy to use, suitable for smaller b2b and B2C buyer journeys.
- Pardot by Salesforce: Specifically designed for B2B marketing automation, excelling in creating and managing lead nurturing programs.
3. Analytics Platforms
These tools provide insights into how customers interact with your marketing efforts. Analytics help refine marketing journey stages and ensure that strategies are aligned with actual customer behavior.
- Google Analytics: A must-have for tracking website traffic and user behavior, offering insights that help refine marketing journey stages.
- Mixpanel: Provides detailed analysis of user interactions with web and mobile applications, helping businesses understand the impact of their marketing efforts.
- Adobe Analytics: Offers advanced segmentation and real-time analytics capabilities, ideal for enterprises needing detailed insights into complex customer journeys.
Integrating these tools helps companies optimize every aspect of the buyer journey, from initial awareness to post-purchase engagement, by providing data-driven insights to tailor strategies effectively.
Common Pitfalls in Understanding the Buyer’s Journey

1. Overlooking Early Stages
One frequent error is neglecting the early stages of the buyer journey, particularly in the b2b buyer journey, where the length and complexity can dilute the focus.
- Awareness: Businesses often miss the chance to effectively educate potential customers about the problem their product or service solves.
- Consideration: Similarly, failing to provide detailed, comparative information during the consideration stage can leave potential buyers under-informed and less likely to progress.
2. Assuming a Linear Process
The buyer’s journey is rarely a straight line, yet many strategies assume it is.
- Multiple Entry Points: Customers might enter the journey at different stages based on prior knowledge or experience.
- Looping: In complex decisions, especially in B2B contexts, buyers may revisit earlier stages before making a final decision. Recognizing and facilitating this loop can enhance the sales journey.
3. Failing to Align Content with Stages
Aligning content with the specific needs of each stage in the buyer’s journey stages is crucial but often mishandled.
- Educational Content in Awareness: Providing general information that helps potential customers understand their problems without pushing for sales.
- Detailed Comparisons in Consideration: Offering in-depth comparisons and case studies that help buyers evaluate their options.
- Strong CTAs in Decision: At the decision stage, clear and compelling calls to action are necessary to convert interest into sales.
4. Ignoring Post-Purchase Opportunities
The journey doesn’t end at purchase, especially in sectors with high potential for repeat business.
- Follow-up Support: Ensuring customers are satisfied post-purchase can transform them into repeat buyers or even brand advocates.
- Leveraging Feedback: Post-purchase feedback is invaluable for refining the buyer’s journey and should be integrated regularly into the marketing strategy.
By understanding and addressing these pitfalls, businesses can significantly improve their approach to the buyer journey. This involves continuous learning and adaptation to meet evolving customer expectations and behaviors, ensuring marketing and sales efforts are as effective as possible.
Grasping the buyer journey is essential for businesses aiming to improve their marketing and sales outcomes. This journey is not just a pathway but a strategic framework that guides potential customers from initial awareness to the final purchase and beyond.
Understanding the buyer journey allows companies to craft targeted strategies that address specific needs at each stage. This tailored approach can significantly enhance the effectiveness of both marketing and sales efforts.
Businesses must stay agile, continually adapting their strategies based on real-time data and feedback. This includes refining buyer’s journey stages, improving customer buyer journey experiences, and optimizing b2b sales journeys.
The dynamic nature of customer behaviors and technological advancements makes it crucial for businesses to remain adaptable. Continuously evolving strategies ensure that companies keep pace with changes in consumer expectations and market conditions.
By deeply understanding and continually adapting the buyer journey, businesses can not only meet but exceed customer expectations, fostering loyalty and driving sustainable growth.

How does the buyer’s journey differ in service vs. product industries?
The buyer journey in service industries often involves more emphasis on relationship building and trust due to the intangible nature of services. In contrast, product industries may focus more on features, benefits, and competitive pricing.
What are the best practices for engaging customers at each stage of the journey?
- Awareness Stage: Use educational content to inform potential customers about their problems and your solutions.
- Consideration Stage: Provide detailed comparisons and case studies to help buyers evaluate your offerings.
- Decision Stage: Offer incentives, robust support, and clear communication to facilitate the purchase decision.
How often should the mapping of the buyer’s journey be revisited?
Regularly review and update the buyer journey mapping to ensure it aligns with current customer behaviors and market trends. This typically happens annually or biannually.
What are the signs that a buyer’s journey mapping is not effective?
Signs include low engagement rates, poor conversion rates, and feedback indicating that customer needs are not being met effectively at different stages.
How can small businesses apply these concepts with limited resources?
Small businesses should focus on clearly understanding their buyer stages and leveraging cost-effective tools like social media and email marketing to engage customers effectively throughout their sales journey.





