Quick Summary
XML sitemaps help search engines index your website effectively. They improve site visibility and crawling efficiency. Learn about the recent updates to Google guidelines on XML sitemaps, which can significantly impact your site’s SEO performance.
An XML sitemap is a file that helps search engines like Google and Bing understand the structure of your website. It lists the URLs of your site and provides additional metadata about each URL, such as when it was last updated and how often it changes. This helps search engines crawl and index your site more efficiently, ensuring that all important pages are discovered and ranked appropriately.
XML sitemaps are essential for search engine indexing because they provide a clear map of your website’s structure. This is particularly beneficial for large websites with numerous pages or complex navigation, as it helps ensure that no important content is overlooked during the crawling process.
Creating and maintaining an XML sitemap can significantly boost your site’s SEO performance. By regularly updating your sitemap, you ensure that search engines always have the latest version of your site’s structure, which can improve your visibility in search results.
Google’s recent updates to its guidelines on XML sitemaps emphasize the importance of including all relevant URLs and keeping the sitemap updated. These updates highlight the need for including hreflang attributes for international content and using canonical URLs to avoid duplicate content issues.
This XML sitemap guide will cover everything you need to know about XML sitemaps, from their definition and benefits to how to create and submit one. We’ll also discuss the latest updates in Google’s guidelines and how to align your sitemap strategy with these changes for optimal SEO performance.
What is an XML Sitemap?

An XML sitemap is a file that lists the URLs of a website, providing detailed information to search engines about the site’s structure and the relationships between different pages. This file uses the Extensible Markup Language (XML) format, making it readable for search engine bots, such as Googlebot, that perform website crawling to index web pages.
Detailed Definition
At its core, an XML sitemap serves as a roadmap of your website, guiding search engines through the various pages and helping them understand the content hierarchy. It contains metadata about each URL, including:
- The date the page was last modified.
- How frequently the page is updated.
- The page’s priority relative to other URLs on the site.
Structure and Components
The structure of an XML sitemap follows a specific format outlined by the sitemaps protocol. Here are the key components:
- XML Header: Indicates the XML version and encoding.
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”UTF-8″?> - URL Set: The container for all URLs.
<urlset xmlns=”http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9″> - URL Entry: Contains details about a specific URL.
<URL>
<loc>http://www.example.com/</loc>
<lastmod>2023-06-01</lastmod>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>- Location Tag (loc): Specifies the URL of the page.
- Last Modified Tag (lastmod): Indicates the last modification date of the page.
- Change Frequency Tag (changefreq): Suggests how often the page content changes.
- Priority Tag (priority): Assigns a priority value between 0.0 and 1.0, indicating the importance of the page.
Differences Between XML and HTML Sitemaps
XML sitemaps and HTML sitemaps serve different purposes. While an XML sitemap is designed for search engines to improve search engine indexing, an HTML sitemap is meant for human visitors to navigate the site. HTML sitemaps typically display a hierarchical list of pages, allowing users to find content easily.
Importance for SEO
XML sitemaps play a crucial role in sitemap SEO by ensuring that search engines can efficiently crawl and index a website’s pages. This is particularly beneficial for:
- Large websites: Helps in indexing numerous pages.
- New websites: Assists in initial crawling when external links are limited.
- Sites with rich media content: Ensures proper indexing of images and videos.
- Sites with complex structures: Helps in better understanding the site hierarchy and relationship between pages.
By creating an XML sitemap and following best practices, website owners can significantly enhance their site’s visibility and ranking in search engine results, making it an essential component of any effective SEO strategy.
Benefits of Using XML Sitemaps

XML sitemaps provide a structured map of your website, offering numerous advantages for search engine optimization (SEO) and overall website performance.
1. Improved Crawlability
One of the primary benefits of an XML sitemap is enhanced crawlability. XML sitemaps help search engine bots efficiently crawl your website by providing a clear, organized structure of your pages. This is especially beneficial for large websites or those with complex navigation, ensuring that all important pages are discovered and indexed.
2. Better Indexing
Sitemaps make it easier for search engines to index your site’s pages by highlighting the content and its structure. This helps search engines understand the relationships between pages, improving the indexing process. By including important pages in your sitemap, you increase the chances of them being indexed and appearing in search results.
3. Enhanced Visibility
Including a comprehensive list of pages in your sitemap can improve your website’s visibility in search engine results. This is crucial for pages that might not be easily discoverable through regular crawling, such as those with limited internal links or pages buried deep within the site hierarchy.
4. Faster Indexing
XML sitemaps can speed up the indexing of new content by providing search engines with information about recent changes and updates. This is particularly important for websites that frequently add new content, such as blogs or news sites. By updating the lastmod tag with the last modification date, you ensure that search engines are aware of fresh content, prompting them to crawl and index it more quickly.
5. Easier Troubleshooting
Sitemaps can help identify issues or errors on your website, such as broken links, missing pages, or duplicate content. By regularly reviewing your sitemap in tools like Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools, you can spot and fix problems promptly, improving the user experience and maintaining the health of your site.
6. Benefits for Specific Types of Content
For websites with rich media content, such as images and videos, sitemaps play a crucial role in ensuring that this content is indexed correctly. By using specific tags for images and videos within your XML sitemap, you can help search engines understand and index these media types, potentially improving their visibility in search results.
In summary, XML sitemaps are an essential tool in the sitemap SEO toolkit, offering numerous benefits that enhance a website’s crawlability, indexing, visibility, and overall search engine performance. Regularly updating and maintaining your sitemap ensures that your website remains optimized and accessible to search engines.
How to Create an XML Sitemap
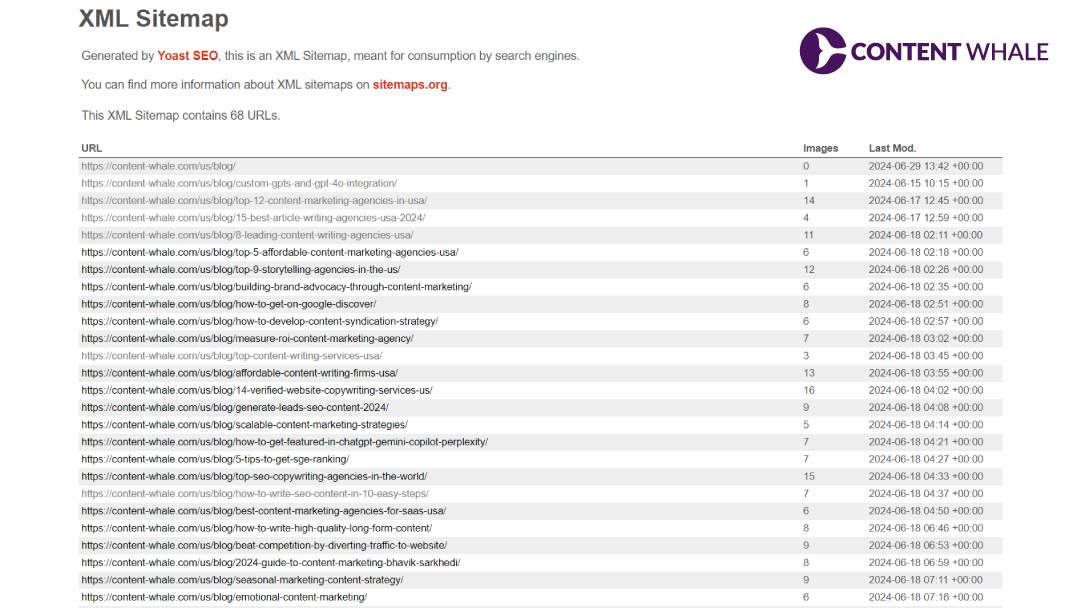
Creating an XML sitemap is essential for optimizing your website’s visibility and performance in search engine results. Here’s a step-by-step XML sitemap guide to help you generate and manage your sitemap effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating an XML Sitemap
1. Using WordPress Plugins
a) Yoast SEO Plugin
- Installation: Install and activate the Yoast SEO plugin from your WordPress dashboard by navigating to Plugins > Add New and searching for “Yoast SEO”.
- Enable XML Sitemaps: Once activated, go to SEO > General > Features tab. Ensure the “XML sitemaps” toggle is turned on and click “Save Changes”.
- View Sitemap: To view your sitemap, click the question mark next to the XML sitemaps toggle and follow the provided link. Your sitemap URL typically follows the structure http://www.yourwebsite.com/sitemap_index.xml.
b) All in One SEO (AIOSEO) Plugin
- Installation: Install and activate the All in One SEO plugin from the WordPress dashboard.
- Enable Sitemap: Navigate to All in One SEO > Sitemaps and ensure the Sitemap feature is enabled. Customize your sitemap settings as needed, such as including or excluding post types and taxonomies.
- Additional Pages: AIOSEO allows adding external pages to your sitemap. Enable this feature in the ‘Additional Pages’ section and add the necessary URLs.
2. Using Online Sitemap Generators
For websites not using WordPress or those requiring manual sitemap creation, online sitemap generators can be very effective.
a) XML-Sitemaps.com
- Access the Tool: Visit XML-Sitemaps.com and enter your website URL in the provided form.
- Generate Sitemap: The tool will crawl your website and generate a sitemap file. Download the file once the process is complete.
- Upload to Server: Use an FTP client like FileZilla to upload the sitemap file to your website’s root directory (e.g., http://www.yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml).
b) Screaming Frog SEO Spider
- Crawl Your Site: Download and install Screaming Frog SEO Spider. Enter your website URL and start the crawl.
- Generate Sitemap: Once the crawl is complete, navigate to Sitemaps > XML Sitemap, configure your settings, and generate the sitemap file.
- Upload and Submit: Upload the sitemap file to your server and submit it to Google Search Console.
Best Practices for XML Sitemaps
- Include Only Important URLs: Ensure that your sitemap includes URLs you want to be indexed, such as key pages and posts. Avoid including noindex pages or duplicate URLs.
- Use the <lastmod> Tag: Update the <lastmod> tag to reflect the last modification date of each URL, helping search engines understand content freshness.
- Regular Updates: Keep your sitemap updated to include new content and remove obsolete URLs. Tools like Yoast SEO and AIOSEO can automate this process.
- Submit to Search Engines: After creating your sitemap, submit it to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to ensure it gets crawled and indexed efficiently.
By following these steps and best practices, you can effectively create and maintain
Submitting Your XML Sitemap to Search Engines
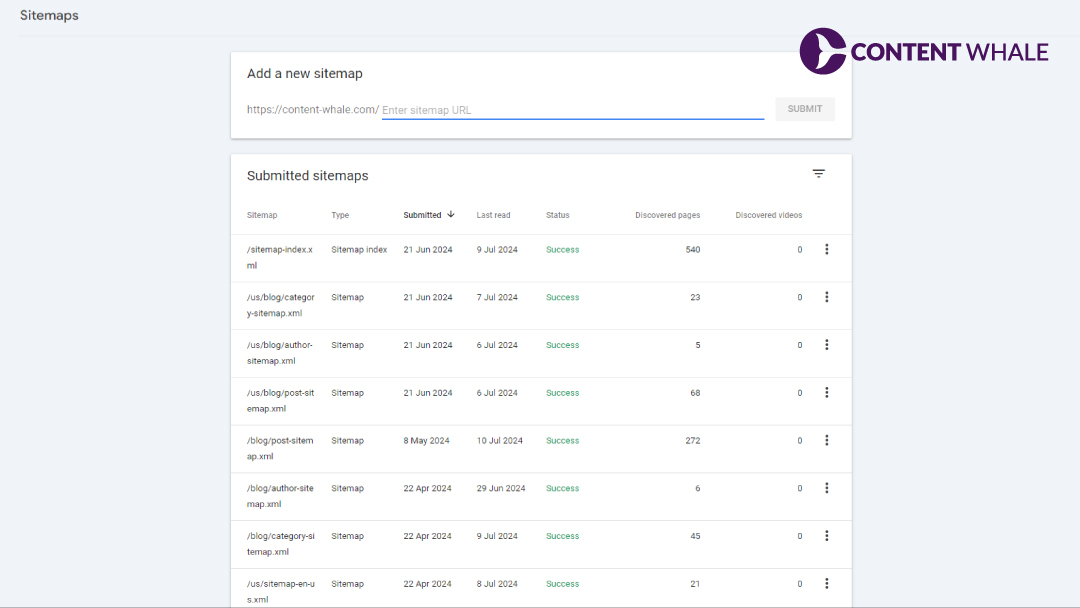
Submitting your XML sitemap to search engines is crucial for ensuring that your website is crawled and indexed efficiently. Here’s a step-by-step guide to submitting your XML sitemap to Google, Bing, and other major search engines.
Submitting Your Sitemap to Google Search Console
- Access Google Search Console: If you don’t have an account, create one at Google Search Console. Log in to your account.
- Add Your Property: In the top-left corner, click on the dropdown menu and select “Add Property”. Enter your website’s URL and click “Continue”.
- Verify Ownership: Choose a verification method, such as adding an HTML tag to your site’s <head> section or uploading an HTML file to your website’s root directory. Follow the instructions provided to complete the verification process.
- Navigate to Sitemaps: Once your property is verified, go to the “Sitemaps” section in the left-hand menu under the “Index” section.
- Submit Your Sitemap: Enter the URL of your sitemap (e.g., https://www.yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml) in the “Add a new sitemap” field and click “Submit”. Google will start processing your sitemap and will notify you of any errors.
Submitting Your Sitemap to Bing Webmaster Tools
- Access Bing Webmaster Tools: Go to Bing Webmaster Tools and log in or create an account.
- Add Your Site: Click on “Add a Site” and enter your website URL. Follow the prompts to verify your ownership using methods similar to Google Search Console.
- Navigate to Sitemaps: In the left-hand menu, click on “Sitemaps” under the “Configure My Site” section.
- Submit Your Sitemap: Enter the URL of your sitemap and click “Submit”. Bing will then process your sitemap, which also helps index your site on Yahoo.
Submitting Your Sitemap to Other Search Engines
Yandex: Create an account on Yandex Webmaster. Add your site and verify ownership using an HTML file, meta tag, or DNS record. Submit your sitemap URL in the “Indexing” section under “Sitemap files”.
Baidu: Create an account on Baidu Webmaster Tools, noting that this process requires a Chinese phone number. Verify your site ownership and submit your sitemap URL.
Using Robots.txt File
You can also inform search engines about your sitemap by including its URL in your robots.txt file. Add the following line to your robots.txt file:
Sitemap: https://www.yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xmlThis helps ensure that search engines discover your sitemap even if you haven’t submitted it directly.
Monitoring and Updating Your Sitemap
Regularly check the status of your submitted sitemaps in Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools. Look for any errors and make necessary updates to your sitemap to ensure all your important pages are indexed properly. It’s also a good practice to update your sitemap whenever you add or remove significant content from your site.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your XML sitemap is effectively submitted and maintained, boosting your site’s visibility and performance in search engine results.
Recent Updates to Google’s Guidelines on XML Sitemaps
Google continues to refine its guidelines to enhance how search engines crawl and index websites. Here are the latest updates and best practices for XML sitemaps in 2026.
Streamlining Image and Video Metadata
Google has recently updated its guidelines to stop supporting certain types of image and video metadata in XML sitemaps. Specifically, captions, titles, and licensing information for images are no longer read by Google. This change helps streamline sitemap files, making them smaller and faster to generate, which is beneficial for large websites with extensive media content.
Emphasis on URL Sequencing
Organizing URLs within sitemaps by their importance and recency has become more critical. Although Google doesn’t always use priority and change frequency tags, placing the most recently modified pages at the top can help ensure they are crawled sooner. This is especially useful for large websites that frequently update their content.
Combining XML Sitemaps with RSS/Atom Feeds
Google now recommends using both XML sitemaps and RSS/Atom feeds. XML sitemaps provide comprehensive details about all pages on a site, while RSS/Atom feeds highlight recent updates. This combination ensures that search engines are promptly informed about new content, improving indexing efficiency.
Best Practices for XML Sitemaps
To align with Google’s updated guidelines, consider the following best practices:
- Include Fetchable URLs Only: Ensure that your sitemap contains URLs that can be fetched by Googlebot, avoiding those blocked by robots.txt or requiring login access.
- Regularly Update <lastmod> Tags: Keep the <lastmod> tags current to reflect the latest changes to your pages, helping Google understand content freshness.
- Avoid Deprecated Properties: Remove deprecated properties such as <image:title> and <image:caption> from your sitemaps.
- Sequence URLs by Importance: Organize URLs by their importance and recency to optimize the crawl budget effectively.
Practical Steps for Implementing Changes
- Audit Your Current Sitemaps: Review your existing sitemaps to ensure they comply with the latest guidelines.
- Use Updated Sitemap Generators: Tools like Yoast SEO and other sitemap generators have been updated to align with these changes, making it easier to generate compliant sitemaps.
- Submit Regularly to Search Engines: Keep your sitemaps up-to-date and submit them regularly to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
- Monitor Performance: Use Google Search Console to monitor the performance of your sitemaps and address any issues promptly.
These updates and best practices help ensure that your website is crawled and indexed efficiently, improving your site’s visibility and performance in search engine results.
Importance of Staying Current with Google’s Webmaster Guidelines for Optimal SEO Performance
Staying up-to-date with Google’s Webmaster Guidelines is essential for maintaining and improving your website’s SEO performance. These guidelines provide the foundation for how search engines index and rank your site, ensuring that your content meets the latest standards for visibility and user experience.
Why Staying Updated Matters
- Algorithm Changes: Google frequently updates its algorithms to improve search results. Keeping up with these changes helps ensure that your site adheres to the latest criteria, preventing sudden drops in rankings due to outdated practices. Regularly monitoring updates and adapting your strategies is crucial to stay ahead in the SEO game.
- Enhanced Search Engine Indexing: By following the latest guidelines, you ensure that your site structure is optimized for efficient crawling and indexing. This includes using an XML sitemap to provide a clear roadmap of your website’s content. An updated XML sitemap guide can help you organize your URLs, making it easier for search engines to find and rank your pages.
- Improved User Experience: Google’s guidelines emphasize the importance of user experience. Factors like page load speed, mobile-friendliness, and high-quality content are critical for retaining visitors and reducing bounce rates. Adhering to these guidelines not only boosts your SEO but also enhances overall user satisfaction.
- Compliance with Google’s Best Practices: Google’s Webmaster Guidelines outline best practices for website crawling and indexing. This includes using sitemap generators and tools like Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to submit and monitor your sitemaps. Regularly updating your sitemaps and ensuring they comply with the latest Google guidelines is vital for maintaining optimal SEO performance.
Practical Steps to Stay Current
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular SEO audits to identify and fix issues that may arise due to algorithm updates. Tools like Google Search Console can help you monitor your site’s health and make necessary adjustments.
- Follow Industry News: Stay informed about the latest SEO trends and Google updates by following reputable SEO blogs and industry experts. This will help you quickly adapt to any changes in the guidelines.
- Optimize Technical SEO: Focus on technical SEO aspects such as site structure, URL sequencing, and metadata optimization. Ensuring that your site is technically sound can significantly improve its performance in search results.
Benefits of Adapting to Updates
- Higher Rankings: Websites that comply with the latest guidelines are more likely to achieve higher rankings in search engine results pages (SERPs).
- Better Visibility: Regularly updated sitemaps and adherence to best practices ensure that your site remains visible to search engines, leading to increased organic traffic.
- Competitive Edge: Staying current with Google’s guidelines gives you a competitive advantage, helping you outperform competitors who may not be as diligent in following updates.
Keeping up with Google’s Webmaster Guidelines is not just about avoiding penalties; it’s about continuously improving your website’s performance and staying ahead in the ever-changing world of SEO. By following these guidelines and adapting to new updates, you can ensure that your site remains optimized for both search engines and users.
Conclusion

Understanding what an XML sitemap is and its role in SEO is essential for any website owner aiming to improve their search engine visibility. An XML sitemap serves as a blueprint for your website, helping search engines like Google to efficiently crawl and index your pages.
XML sitemaps are particularly beneficial for large websites, sites with isolated pages, new websites with few external links, and sites with rich media content. They ensure that all important pages are indexed and help search engines understand the site structure, leading to better search engine rankings.
Creating an XML sitemap is straightforward, especially with the numerous sitemap generators and plugins available. Regularly updating and submitting your sitemap to search engines ensures that your new and updated pages are indexed promptly. Tools like Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools can help you monitor and manage your sitemap submissions effectively.
Staying updated with Google guidelines and best practices for sitemaps is crucial for maintaining optimal SEO performance. A well-maintained XML sitemap not only enhances search engine indexing but also improves the overall user experience by ensuring that your most valuable content is discoverable.
By following this XML sitemap guide and implementing the outlined strategies, you can significantly enhance your website’s SEO, visibility, and performance.
FAQs
What is an XML Sitemap and Why Do I Need One?
An XML sitemap is a file that lists the URLs of your website, providing search engines with a roadmap of your site’s structure. It helps search engines understand the content and relationships between pages, making it easier to crawl and index your site. This is especially beneficial for large websites, new websites with few backlinks, and sites with rich media content. By ensuring all your important pages are indexed, an XML sitemap can significantly improve your website’s visibility and SEO performance.
How Do I Create an XML Sitemap for My Website?
Creating an XML sitemap can be done using various methods. For WordPress users, plugins like Yoast SEO can automatically generate a sitemap. Other options include online tools like XML-Sitemaps.com and Screaming Frog SEO Spider. These tools crawl your website and generate a sitemap file, which you can then upload to your server. Once created, you should submit the sitemap to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to ensure it is crawled and indexed properly.
What are the Benefits of Using an XML Sitemap for SEO?
An XML sitemap offers several benefits for SEO:
- Improved Crawlability: Helps search engine bots efficiently crawl your site.
- Better Indexing: Ensures all important pages are indexed.
- Enhanced Visibility: Increases the likelihood of your pages appearing in search results.
- Faster Indexing: New content is discovered and indexed more quickly.
- Easier Troubleshooting: Identifies issues like broken links and duplicate content.
How Do I Submit My XML Sitemap to Search Engines?
To submit your XML sitemap to Google, follow these steps:
- Log in to Google Search Console.
- Select your property.
- Navigate to the “Sitemaps” section.
- Enter the URL of your sitemap (e.g., https://www.yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml).
- Click “Submit.”
For Bing, use Bing Webmaster Tools and follow a similar process to submit your sitemap. Regularly check for errors and updates in your sitemap submissions to ensure continuous indexing.
What Are the Recent Updates to Google’s XML Sitemap Guidelines?
Recent updates to Google’s guidelines emphasize streamlining sitemaps by excluding certain metadata, like image titles and captions. They also recommend using both XML sitemaps and RSS/Atom feeds for comprehensive indexing. Prioritizing URLs by importance and keeping the sitemap updated with the latest content changes are crucial for maintaining effective SEO.
Do I Need an XML Sitemap if My Website is Small?
While small websites (less than 500 pages) with comprehensive internal linking might not require an XML sitemap, it is still beneficial. A sitemap ensures that all your pages are indexed and provides a clear structure for search engines. Even for smaller sites, having an XML sitemap can aid in better indexing and visibility.





